Bank lending and exchange rate shocks
7 min readThorsten Beck, Peter Bednarek, Daniel te Kaat, Natalja von Westernhagen 25 April 2022
Current economic analysis works by using common open macro products to gauge the effect of trade price improvements on the real economic climate, but these designs normally ignore the position of the money process. Empirical proof has proven, even so, that the publicity of corporations and economic institutions to international forex property and liabilities can also engage in an important role in the impact of trade fee actions on the true financial state (Bruno and Shin 2021, Calomiris et al. 2022). How do banks’ foreign currency exposure affect their lending, their borrowers’ expenditure and economic advancement? In recent function (Beck et al. 2022), we exploit the euro depreciation of 2014 to gauge how this unpredicted and exogenous exchange charge movement affected the lending behaviour of German banks, the function of interbank markets, firms’ expense behaviour and regional progress general performance.
We conjecture that exchange rate shocks must influence lender mortgage provide when financial institutions have international currency exposure on their balance sheets that is not properly hedged. Precisely, a European financial institution with better volumes of international forex property than liabilities activities an improve in web truly worth because of the US greenback appreciation (corresponding to the euro depreciation) and is, as a result, most likely to expand credit rating provide. Policymakers therefore will have to thoroughly think about each the overseas forex publicity of the banking method and the distribution throughout financial institutions when assessing the effects of exchange charge adjustments on the true financial system.
The placing
The Federal Reserve’s tapering induced a sharp depreciation of the euro towards the US dollar. Specially, involving 2014 Q2 and 2015 Q1, the euro lost marginally far more than 20% in benefit relative to the dollar (see Figure 1). This depreciation was largely unanticipated for fiscal market participants as the change in shorter-expression interest amount forecasts involving the euro area and the US had been fairly secure.
Whilst it is unattainable to attribute this exchange fee motion to just 1 single issue, several forex dealers defined it by a increase in the greenback, driven at the very least to a massive extent by the gradual reversal of the quantitative easing coverage in the US, recognized as the Federal Reserve’s tapering, whilst the ECB ongoing its buys of economical belongings. Whilst German financial institution lending conduct is highly not likely to affect the stance of financial plan in the US for evident good reasons, the ECB’s conclusion to expand its lax monetary plan was less driven by the German financial circumstance than macroeconomic fundamentals in Southern Europe (Iletzki et al. 2020).
Germany is an appealing laboratory for studying the effects of this trade fee motion on the genuine economic system by way of the banking sector for the reason that the German banking sector experienced accrued sizeable quantities of internet foreign forex property in the mixture but with pronounced cross-bank variation. At the exact time, Germany is an export-intensive economic system with a person of the premier web export to GDP ratios in the globe. Therefore, trade rate changes are most likely to have sizeable serious outcomes.
Determine 1 The euro/US dollar exchange fee in excess of time
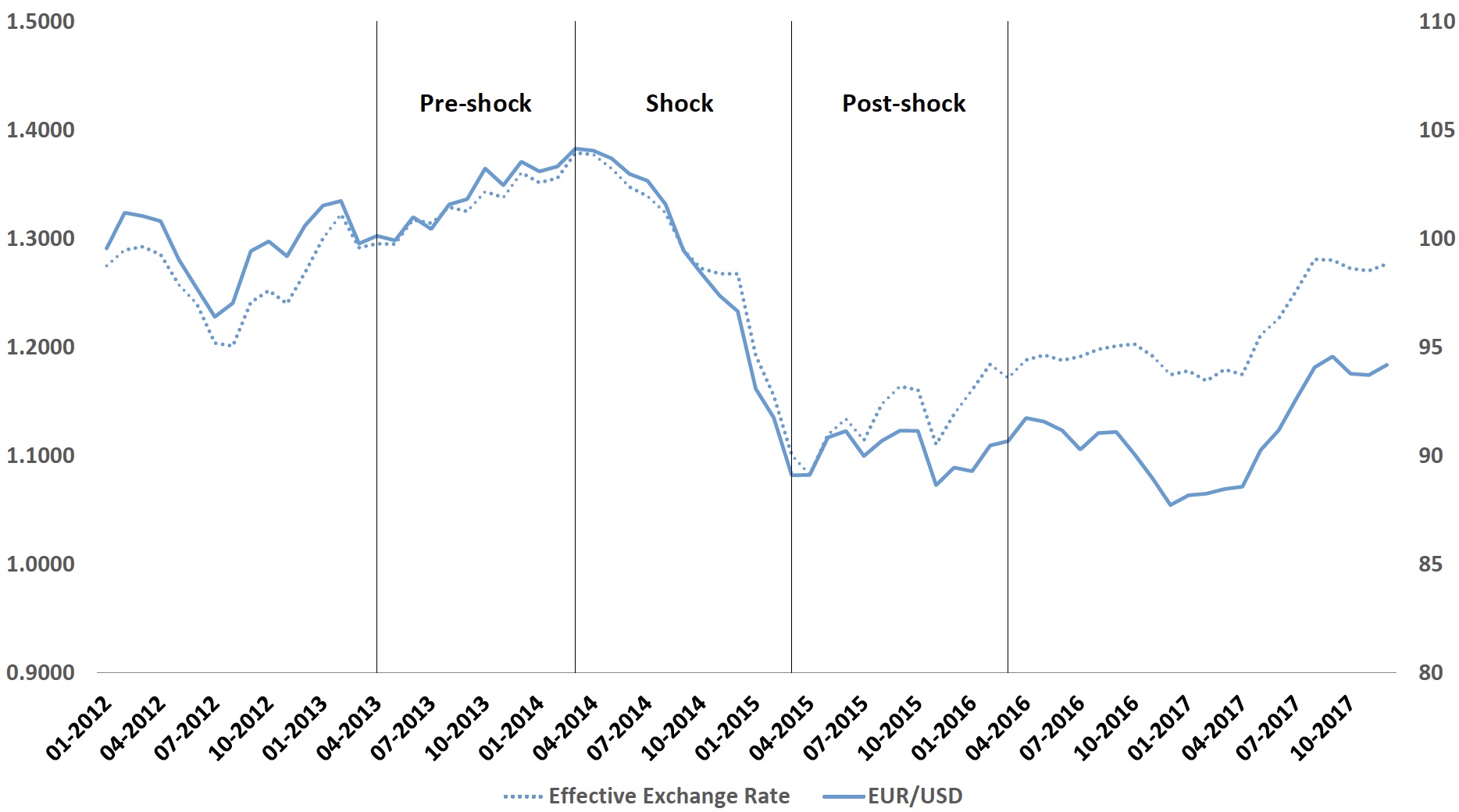
Note: This determine exhibits the month to month dynamics of the EUR/USD trade amount and of the trade weighted nominal productive trade rate (1999 Q1=100) about the depreciation episode of 2014 Q2-2015 Q1. Data sources: Federal Reserve Financial institution of St. Louis and ECB.
Knowledge and empirical approach
We use two unique datasets: one at the lender-firm-financial loan degree and one particular at the location stage. The financial institution-agency-loan-stage dataset is at quarterly frequency and combines Deutsche Bundesbank’s credit registry with company-degree info from Amadeus and lender-amount data from the Bundesbank. The latter also incorporates detailed facts about banks’ overseas forex asset holdings. The regional dataset combines details from the INKAR databases, which contains details on all 401 administrative areas in Germany at annual frequency, with equilibrium sheet characteristics of regional financial institutions.
We estimate big difference-in-difference regressions all-around the depreciation episode of 2014 Q2-2015 Q1, evaluating the pre-depreciation interval (2013 Q2-2014 Q1) to the publish-depreciation period of time (2015 Q2-2016 Q1). Our empirical tactic relies on the differential, pre-shock publicity of German banks to internet US greenback property (scaled by whole assets), with banking companies acquiring better foreign currency property currently being more uncovered.
When researching the cross-agency dissimilarities in credit allocation, identification also hinges on the heterogeneity of firms’ pre-depreciation stability sheet features. Subsequent the standard method in the credit registry literature, we even more limit our sample to corporations with numerous bank associations and contain company set outcomes to hence control for bank loan desire and isolate provide results (Khwaja and Mian 2008).
We also distinguish among lender lending to firms and to other banks to isolate the outcome of the exchange fee depreciation on the interbank market. To analyze no matter if the extra mortgage source following the depreciation spills around to the serious economic climate, we enhance these regressions with company-degree estimations of credit score progress, financial commitment, and employment, as nicely as location-degree estimations of GDP growth.
Our location-level regressions rely on a distinctive element of the German banking method, in that personal savings banks (the major of the three pillars of the German banking process) are constrained to distinct geographic locations and we can therefore map their lending to expansion in 401 administrative regions in Germany.
Outcomes
Our examination presents three principal success.
Very first, the euro depreciation encourages larger sized banking companies with major internet foreign currency asset exposure to develop their credit source. Dependent on the lender dimension definition, we locate a huge lender with a one percentage position bigger internet foreign currency asset share than the median huge bank has a 4.5-5.5 proportion point increased credit score progress (this compares to median credit rating progress of -7.1% involving 2013-14 and 2015-16).
Second, this improve can be explained by progress in financial loan offer to export-intense firms, not to riskier companies, and, even more essential, by an maximize in interbank current market action. In distinct, massive banking institutions with considerable internet overseas forex belongings increase their interbank lending to compact banking institutions without having major foreign currency asset publicity, but with a higher share of exporting corporations in their credit portfolio, which in change also lets smaller banks to extend their credit rating supply. This is evidence that the trade price depreciation, by escalating the liquidity of distinct tiers of the domestic banking sector, can have sizeable financial outcomes, even when nearby banking institutions have reduced overseas currency asset publicity and are as a result not affected straight by the exchange charge shock.
Third, we exhibit that exporting firms borrowing from more compact banking companies with greater interbank current market dependence maximize their investment decision pursuing the trade level depreciation and that locations with community financial institutions benefiting from this maximize in interbank borrowing expertise considerably greater GDP development than a lot less exposed regions. In economic phrases, we exhibit that a lot more uncovered regions develop by 1.3-1.4 percentage details much more than considerably less exposed regions, cumulatively, in the two several years after the depreciation relative to the two pre-depreciation decades, which compares to a median expansion fee of 11.9%. Hence, exchange charge movements, by shifting the composition of lender financial loan source and raising interbank liquidity, can have sizeable combination implications.
In sum, large banks whose internet really worth enhanced since they held higher internet international currency belongings improved lending, including via interbank markets to smaller banks with a higher share of exporting firm borrowers. This in switch resulted in greater investment decision by such companies and in regions more compact banking institutions obtaining additional interbank financial loans.
Contribution and coverage implications
Our benefits communicate to the literature on the impact of exchange fee modifications on the true financial system. Although there is abundant proof displaying that exchange price depreciations can decrease organization financial commitment and genuine economic advancement when firms have foreign currency personal debt (e.g. Aguiar 2005, Kearns and Patel 2016, Du and Schreger 2022, Kalemli-Ozcan et al. 2021), only a person review, at minimum to the most effective of our expertise, seems to be at how the development consequences of exchange rate actions are influenced by banks’ foreign currency exposure. Precisely, Agarwal (2019) reveals that exchange fee depreciations (appreciations) can direct to an raise (lessen) in domestic credit score and increased (lower) aggregate development when the domestic banking sector has significant net foreign currency asset publicity.
Our contribution to the literature is that with the use of granular financial institution-agency-loan-degree knowledge we can supply proof for particular mechanisms by means of which exchange charge adjustments can affect mortgage provide, i.e., by way of immediate lending and interbank lending, and connection these mechanisms to serious financial consequences.
The coverage implications of our analysis are that the consequences of trade level alterations are not restricted to people predicted by common versions of open macroeconomics, but are critically impacted not only by the aggregate equilibrium sheet framework of a country’s banking system, but the efficiency of its interbank industry. Policymakers need to choose into account these further channels when evaluating the affect of trade level modifications on banking techniques and real financial system.
References
Agarwal, I (2019), “Banks’ International Currency Exposure and the Actual Consequences of Trade Rate Shocks”, mimeo, College of British Columbia.
Aguiar, M (2005), “Investment, Devaluation, and Overseas Currency Exposure: The Scenario of Mexico”, Journal of Progress Economics 78(1): 95–113.
Beck, T, P Bednarek, D te Kaat and N von Westernhagen (2022), “The Authentic Results of Exchange Rate Depreciation: The Role of Lender Mortgage Supply”, CEPR Discussion Paper 17231.
Bruno, V and H S Shin (2015), “Dollars and exports: The outcomes of currency power on intercontinental trade”, VoxEU.org, 27 July.
Calomiris, C, M Larrain, S Schmukler and T Williams (2022), “The article-2008 boom in overseas forex corporate bonds: Why emerging markets go large” VoxEU.org, 28 February.
Du, W and J Schreger (2022), “Sovereign Risk, Forex Danger, and Company Stability Sheets”, Overview of Financial Scientific studies, forthcoming.
Kalemli-Ozcan, S, X Liu and I Shim (2021), “Exchange Charge Fluctuations and Agency Leverage”, IMF Economic Critique 69: 90–121.
Kearns, J and N Patel (2016), “Does the Economic Channel of Exchange Premiums Offset the Trade Channel?”, BIS Quarterly Overview.
Khwaja, A I and A Mian (2008), “Tracing the Influence of Bank Liquidity Shocks: Evidence from an Emerging Market”, American Economic Critique 98 (4): 1413–42.